Krafton Jungle/5. PintOS
[PintOS 3주차] Day 1-2
munsik22
2025. 5. 23. 14:28
핀토스 2번째 프로젝트는 2주간 진행된다. 따라서 핀토스 3주차는 이전 주차의 팀과 프로젝트를 그대로 이어서 진행한다.
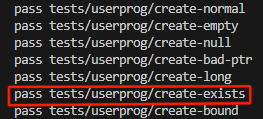
create-exists 해결하기
int process_wait (tid_t child_tid UNUSED) {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < (1<<31); i++) {
}
return -1;
}wait하는 시간을 기존 시간의 2배 정도로 늘려주었더니 pass를 받았다. 하지만 이 방법은 어디까지나 임시방편으로, process_wait()은 child process가 종료될 때까지 기다리는 기능을 수행하도록 수정해야 한다.
이제 진짜 fork, wait, exec 구현을 시작해보자
🔹 process_wait() 구현
process_wait()child_tid를 사용해 child process의 디스크립터 찾기- 호출자는 child process가 exit할 때까지 block된다.
- child process가 exit하면 child process의 디스크립터를 해제하고 child process의 exit status를 리턴한다.
- Semaphore
struct thread에 wait를 위한 세마포어 추가하기- 스레드가 처음 생성되면 세마포어는
0으로 초기화됨 wait(tid)에서, tid의 세마포어에 대해sema_down을 호출tid프로세스의exit()에서,sema_up을 호출sema_down과sema_up을 어디에 호출해야 할까?
- Exit status
struct thread에 exit status를 알리는 필드 추가하기

/* threads/thread.h */
struct thread {
tid_t tid;
…
int exit_status;
bool is_waited;
struct list children;
struct list_elem c_elem;
struct semaphore c_sema;
…
}
🔹 duplicate_pte() 구현
- TODO에 적혀 있는 내용을 그대로 코드로 구현하기만 하면 된다.
static bool duplicate_pte (uint64_t *pte, void *va, void *aux) {
struct thread *current = thread_current ();
struct thread *parent = (struct thread *) aux;
void *parent_page;
void *newpage;
bool writable;
/* 1. TODO: If the parent_page is kernel page, then return immediately. */
if (is_kernel_vaddr(va)) return true;
/* 2. Resolve VA from the parent's page map level 4. */
parent_page = pml4_get_page (parent->pml4, va);
if (parent_page = NULL) return false;
/* 3. TODO: Allocate new PAL_USER page for the child and set result to NEWPAGE. */
newpage = palloc_get_page(PAL_USER);
if (newpage == NULL) return false;
/* 4. TODO: Duplicate parent's page to the new page and
* TODO: check whether parent's page is writable or not (set WRITABLE
* TODO: according to the result). */
memcpy(newpage, parent_page, sizeof(newpage));
writable = is_writable(pte);
/* 5. Add new page to child's page table at address VA with WRITABLE permission. */
if (!pml4_set_page (current->pml4, va, newpage, writable)) {
/* 6. TODO: if fail to insert page, do error handling. */
palloc_free_page(newpage);
return false;
}
return true;
}gdb로 테스트 해보기
pintos를 --gdb 옵션을 설정해서 실행한다.
$ pintos --gdb --fs-disk=10 -p tests/userprog/fork-once:fork-once -- -q -f run fork-once다른 터미널을 열어 gdb를 실행한다.
$ gdb kernel.o
(gdb) target remote localhost:1234
Remote debugging using localhost:1234
0x000000000000fff0 in ?? ()
(gdb) b syscall_handler
Breakpoint 1 at 0x800421d570: file ../../userprog/syscall.c, line 51.
(gdb) b process_wait
Breakpoint 2 at 0x800421c184: file ../../userprog/process.c, line 301.
(gdb) c
Continuing.Breakpoint 설정 후 프로그램을 실행해 보았다.
Breakpoint 2, process_wait (child_tid=128) at ../../userprog/process.c:301
warning: Source file is more recent than executable.
301 process_wait (tid_t child_tid UNUSED) {
(gdb) n
306 struct thread *curr = thread_current();
(gdb) n
307 struct thread *child = NULL;
(gdb) n
309 for (e = list_begin(&curr->children); e != list_end(&curr->children); e = list_next(e)) {
(gdb) n
316 if (child == NULL) return -1;
(gdb) n
326 }
(gdb) n
run_task (argv=0x8004227900 <argv+32>) at ../../threads/init.c:252
252 printf ("Execution of '%s' complete.\n", task);
(gdb) n
253 }
(gdb) n
run_actions (argv=0x8004227900 <argv+32>) at ../../threads/init.c:297
297 argv += a->argc;
(gdb) n
279 while (*argv != NULL) {
(gdb) n
300 }
(gdb) n
main () at ../../threads/init.c:125
125 if (power_off_when_done)
(gdb) n
126 power_off ();
(gdb) n
Remote connection closed
(gdb) qfork-once 프로그램이 시작하자마자 process_wait()이 제일 먼저 실행된다는 것을 볼 수 있었다. fork를 하기도 전이므로 당연히 child process를 가지고 있지 않기 때문에 조건문에 의해 -1을 리턴하며 바로 프로그램이 종료되었다.

/* threads/init.c */
static void run_task (char **argv) {
const char *task = argv[1];
printf ("Executing '%s':\n", task);
if (thread_tests){
run_test (task);
} else {
process_wait (process_create_initd (task));
}
printf ("Execution of '%s' complete.\n", task);
}run_task()에서 process_wait(process_create_initd(task));가 실행된다. 즉, 태스크 실행 흐름은 다음과 같다.
run_task()
├process_wait()
│├process_create_initd()
││├thread_create()
││└returntid
│└returntid
└💥child == NULL → return-1
terminated
[run_task] curr->tid = 1
[process_create_initd] tid = 3
[process_wait] child_tid = 3, curr->tid = 1로깅을 통해 process_wait(process_create_initd(task))에서 current thread의 tid는 1, fork_once의 tid는 3이라는 것을 발견했다. wait으로 리턴하기 전에 fork_once(3)를 run_task(1)의 child로 설정하면 문제를 해결할 수 있지 않을까?